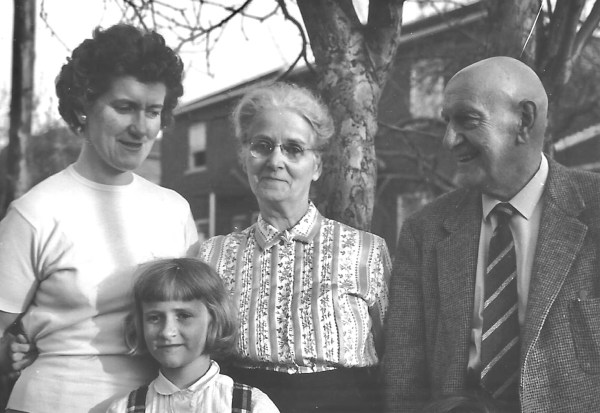
I never met Harry Jolliffe. I never even knew Harry Jolliffe. So, why a story about an unknown man?
We met Hazel and Roger 35 years ago when they would regularly visit us as friends from our church until they moved from Beaconsfield to Salt Lake City, Utah to be with the family. As we are all British we have had a very comfortable friendship over all these years. We now keep in touch via FaceTime. During the last call, we got on to the subject of families and the Mormon practice of marriage being for the eternities and not ‘Till death do us part’.
In The Church of Jesus Christ of Latter-day Saints, the word sealing refers to the joining together of a man and a woman and their children for eternity. This sealing can be performed only in a temple by a man who has the priesthood, or the authority from God. (1)
Roger then told us a story about a conversation he had with a church member, Harry Jolliffe, back in England in 1975, which has haunted him ever since. I was so fascinated by Roger’s story I felt I had to write it down.
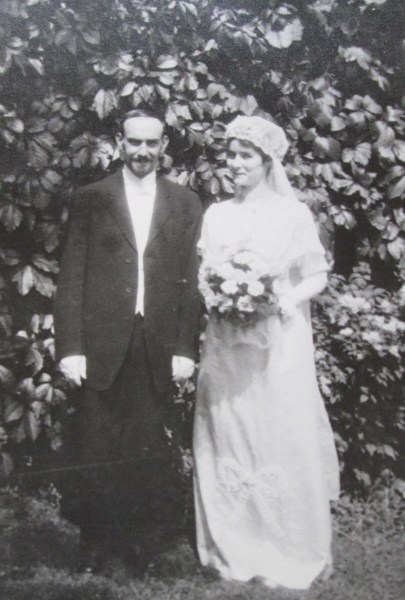
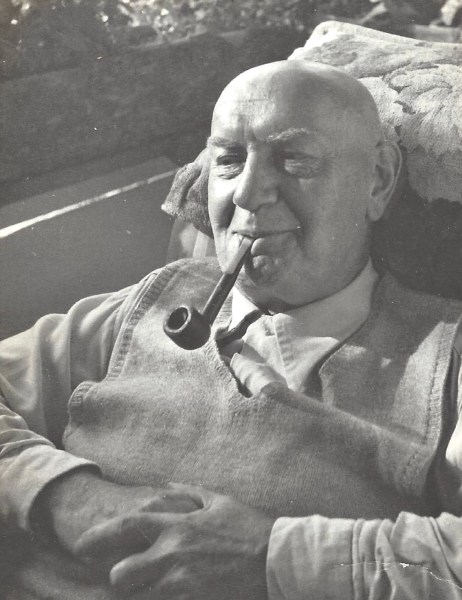
Our friends went to Harry Jolliffe’s home as a representative of their church in 1975, to establish if there were any needs. Harry was 79 years old and had only joined the church 3 months prior. He lived on his own and was still grieving the loss of his wife who had passed away the year before. Roger and his family had only been in the church for a year themselves and knew the challenges of embracing a new faith and wondered what had inspired Harry to join, particularly at his age. Harry then told Roger the harrowing story of his time in a Japanese prisoner-of-war camp
Although captured in Singapore – see below – I cannot read Japanese for the camp Harry was at or of him being sent to any other of the numerous Japanese POW camps on the island of Singapore.
Harry had joined the regular army in the early 1930s and rose to the rank of Warrant Officer in physical training. He was serving in Singapore when the war broke out with Japan. Harry, along with thousands of troops and civilians were swept up and captured.
Below is Harry’s record of his capture at the Racecourse, Singapore, on the 11th of February, 1942. (2)
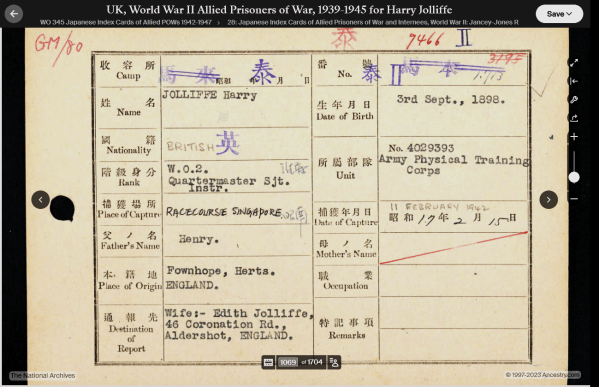
Harry’s Japanese Index Card of Allied POW 1942 – 1947
After his capture, Harry was then imprisoned in a very squalid Japanese prisoner-of-war camp where both British and Australian troops were prisoners. Starved and ill-treated, many died of neglect, abuse or forced labour.
However, because Harry was physically fit he was used as a boxing opponent for the prison guards to spar with and humiliate in front of their comrades and all the other prisoners. He was given slightly better food in order to keep him fit but was warned to always lose each fight so that the Japanese soldiers would not lose face.
While in the camp Harry became gravely ill and was so sick he went to the hut of an Australian prisoner who was a Doctor. This Doctor had previously removed his own appendix with no anaesthetic or suturing material. The Doctor told Harry, that he thought it may have been a gallbladder infection and to come back the next day. Harry returned the next day, with a fever, and feeling much worse.
The Doctor told him the gallbladder had to come out or Harry would die. As he said these words, four burly prisoners entered the room and held Harry down. The Doctor made the first incision. Harry fainted. When he came to, he looked down and saw all his organs displayed on his stomach, and he fainted again. He came to in his hut, his wound had been sutured with string!
He was at least still alive thanks to the skill of the unknown heroic Australian Doctor. He was weak, and all his fellow prisoners had to feed him, was rice water. Harry wanted to die and end his misery.
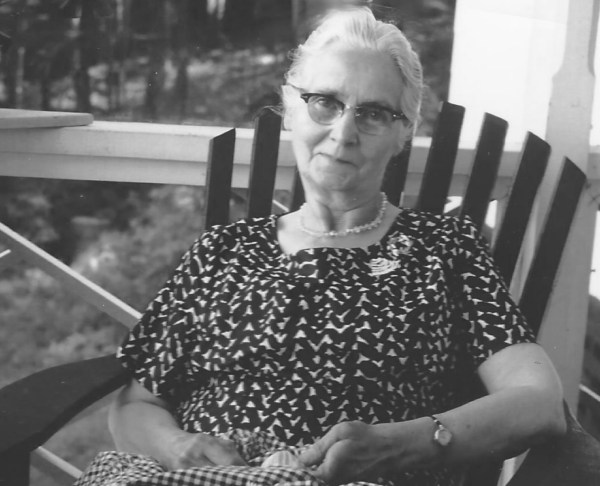
That night, Harry had a fevered dream. He was walking up the street to his home, in England. He opened the gate and knocked on the door. Harry’s wife, Edith said ” Oh! Harry! We missed you so much and we need you!’ Harry awoke and immediately felt a very strong will to live and survive. Singapore was liberated by Australian and US forces in 1945, as the war in the Pacific turned in favour of the Allies, and the prisoners were freed. Harry went home to England, via Southampton, where his wife, Edith, met the ship.
She rushed into his arms, and said “Before you say another word, what happened to you, on this date?” Edith continued ” I had a very vivid experience, I heard a knock on the door, and when I opened it, there you were! I thought I was dreaming but you disappeared as I opened my arms to you! I was fully awake. What happened, Harry”? So, Harry related the story, that on that date a gall bladder operation had been performed on him, and he nearly died, but he believed he survived because of that dream.
To our friends, he said “You asked me why I joined the church. The feeling I had during that dream, which stuck with me all my life, was the same feeling I felt when the missionaries were teaching me about the gospel of Jesus Christ”
He had such a strong desire to listen to these young missionaries and when they mentioned that he could be sealed to his wife for eternity, he readily accepted their teachings. Unfortunately, Harry never lived long enough to carry out his wishes to be sealed for eternity to Edith.
Roger believes the story has haunted him all these years because he is meant to do the sealing of Harry and Edith, vicariously. This is the purpose of the Latter-Day Saints temples, to seal together a family for eternity. Our friends have now done the sealing for Harry and Edith.
Below is a photo of British Prisoners of War after liberation in Singapore.

So, not only is Harry’s story inspiring in a spiritual sense, but also a reminder of the bravery of all those prisoners and civilians who endured the most wretched of circumstances.
I am grateful that Roger shared this story with me, thank you.
SOURCES
(1) https://newsroom.churchofjesuschrist.org/article/sealing
(2) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Fall_of_Singapore
The Surrender of Singapore 1942

Lieutenant-General Arthur Ernest Percival, led by a Japanese officer, walks under a flag of truce to negotiate the capitulation of Allied forces in Singapore, on 15 February 1942. It was the largest surrender of British-led forces in history.