with additional research by Justin Bur
The Mile End neighbourhood of Montreal is famous as the home of Montreal bagels and of novelist Mordecai Richler. Its iconic architecture features outside staircases attached to two- and three-storey rowhouses, next door to churches, synagogues, shops, cafés and renovated manufacturing buildings. But Mile End’s history goes back to one small tavern at a crossroads in the countryside more than 200 years ago.
The Mile End Tavern was located at today’s northwest corner of Saint Laurent Boulevard and Mount Royal Avenue,1 now the starting point of the Mile End neighbourhood. In turn, Mile End is on the Plateau, an elevated plain lying north of Sherbrooke Street and east of Mount Royal.
The first known reference to Mile End was dated April 21, 1808, when landowner John Clark placed a notice in the Gazette advertising Mile End Farm as providing “good pasture for horses and cows at the head of the Faubourg [suburb] Saint-Laurent.”

Clark (1767-1827), an English-born butcher, acquired the land he would call Mile End Farm in several transactions, including purchase agreements and leases, between 1804 and 1810.2 Like most farms in Quebec, it was long and narrow. At its greatest extent in 1810, it measured 2.5 kilometers from south to north, and between 400 and 550 meters wide. Clark was almost certainly the one who chose the name Mile End. The centre of his property was about a mile north of the small city of Montreal, and the area might have reminded him of another Mile End, a mile east of London, England. The name caught on and has been in use ever since.

When Montreal was founded in 1642, Mile End was probably uninhabited. The ground was too rocky for settlements or agriculture, and few Indigenous artefacts have been found there. The northeastern region of the Island of Montreal was covered by a vast cedar forest. The heart of Mile End was also forested, but there, both cedar and ash trees were the dominant species. This forest was still intact when the Sulpician priests mapped the area in 1702, but as the city’s population grew — it stood at around 1,200 residents in 1700 – more and more trees were cut to provide firewood.
By 1780, most trees had disappeared from the foot of the mountain, replaced by houses, farm buildings, hay fields and pastures. In the Mile End area, livestock pastures, vegetable crops, tanneries and quarries dominated the countryside, and orchards were planted in the mid-1800s.
In 1663, the Sulpician priests became the seigneurs, or feudal lords, of the entire island. In 1701, the Hôpital Général acquired an extensive piece of land from the Sulpicians in the future Mile End area, and the Grey Nuns took over the hospital and all its lands in 1747. In 1803, the nuns sold the piece of land that would become Mile End Farm to two masons, Jean-Baptiste Boutonne and Joseph Chevalier. They wanted to quarry its stone and sand for building materials.
The masons had to pay the Grey Nuns a rente constituée (annual interest), as well as yearly seigneurial dues to the Sulpicians. So when John Clark bought the property – the first part of his Mile End Farm — in 18044 and gave Boutonne and Chevalier the right to continue collecting building materials for seven years after the sale, they must have been relieved. Meanwhile, Clark found another use for the land, first advertising pasture for other peoples’ cows in 1808.
When the same ad for livestock pasturing at Mile End Farm appeared the following year, it was placed by Phineas Bagg (c.1751-1823) and his son Stanley Bagg (1788-1853), my four-times and three-times great-grandfathers. A farmer from western Massachusetts, Phineas had brought his family to Canada around 1795. Initially he worked as an innkeeper in LaPrairie, near Montreal, and then the family moved onto the island. In 1810, Phineas and Stanley signed a lease with John Clark.5 Paying an annual rent of 112 pounds, 10 shillings, they ran the Mile End Tavern and managed the farm for the next seven years before subletting to another innkeeper.
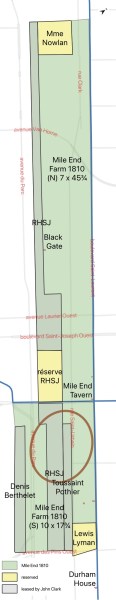
The lease described the property as having a two-storey house (which at some point must have been converted into the tavern), a barn, stable and outbuildings. The Baggs were required to sufficiently manure the pastures and arable land, to cultivate and to perform road maintenance and other required duties. They were permitted to cut wood for fencing and firewood, but they had to preserve the maple grove. They were also permitted to cut and remove stone.
No doubt the tavern brought them a good income since it was located at an important, if somewhat remote, intersection. Stanley must have attracted many additional customers after he built a racetrack nearby. In May 1811, he signed an agreement with the Jockey Club of Montreal, subletting a piece of land to the club and promising to build the track within five weeks. The club supervised the races. The track, partially on land leased from the Sisters of the Hôtel-Dieu, was about a mile in circumference and what is now Jeanne Mance Park, extending east to Saint-Laurent. It was most likely the first racetrack in Montreal.6
Another reference to Mile End appeared in the Gazette on August 4, 1815 when Stanley Bagg, Mile End Tavern, placed a notice offering a reward for information about a lost bay horse, about 10 years old, with a white face and some white about the feet.7
In 1819, Stanley married John Clark’s daughter, Mary Ann (John Clark was also my four-times great-grandfather). Their son, Stanley Clark Bagg (1820-1873), eventually inherited the Mile End Farm, as well as other properties Clark had owned nearby.
In the second half of the 19th century, Stanley Clark Bagg began subdividing and selling the properties he had inherited from his father and grandfather. He died in 1873 and the next generation of the family continued to sell building lots from the Stanley Clark Bagg Estate.
In 1891, they sold most of the Mile End Farm property to McCuaig and Mainwaring, a pair of promoters from Toronto who envisioned a high-end residential suburb they called Montreal Annex.8 The project got off to a slow start because basic services such as water, sewers and streetlights were nonexistent and a promised electric tramway did not materialize in time. A recession that started in 1893 put an end to their dreams. A few years later another group of investors, the Montreal Investment & Freehold Company, took over the property and the area developed as a mixture of duplexes, triplexes and commercial buildings.
Meanwhile, the Mile End Hotel continued to appear in city directories at the corner of Saint- Laurent and Mount Royal until 1900. The property was expropriated for road widening in 1902 and the building was demolished. A department store had replaced it by 1906.
Description of Map: The areas with a greyish tinge are the areas that John Clark held by lease rather than owning them; none of them ever came back to Clark-Bagg possession after the leases ended. The yellow areas are cutouts belonging to and reserved by other people, excluded from the rectangles describing the property leased to P & S Bagg in 1810. Mile End Farm was bounded by the modern Saint-Laurent Blvd. in the east, while the future Park Avenue was just to the west and Pine Ave. would have been the southern boundary. RHSJ refers to the Religieuses Hospitalières de Saint-Joseph de Montréal, a religious order dedicated to caring for the sick.
This article also appears in my personal family history blog, www.writinguptheancestors.ca.
See also:
Janice Hamilton, John Clark, 19th Century Real-Estate Visionary, Writing Up the Ancestors, May 22, 2019, https://www.writinguptheancestors.ca/2019/05/john-clark-19th-century-real-estate.html
Janice Hamilton, The Life and Times of Phineas Bagg, Writing Up the Ancestors, Oct. 17, 2018, https://www.writinguptheancestors.ca/2018/10/the-life-and-times-of-phineas-bagg.html
Janice Hamilton, The Life and Times of Stanley Bagg (1788-1853), Writing Up the Ancestors, Oct. 5, 2016, https://www.writinguptheancestors.ca/2016/10/the-life-and-times-of-stanley-bagg-1788.html
Notes and Sources
1. Mount Royal Avenue is the continuation of Côte Sainte-Catherine Road, which traverses the northeast slope of Mount Royal and continues east of Saint-Laurent Boulevard. Saint- Laurent, now a busy commercial street, was at one time the only road leading north from city to the Rivière des Prairies, on the north shore of Montreal Island. Built by the Sulpician priests in 1717, Saint Laurent was initially known as Le grand chemin du Roy – the Great King’s Highway. Over the years it has been known by many names, English and French, including Chemin Saint-Laurent, St. Lawrence Street and “the Main”. Since 1905, its official name has been Boulevard Saint-Laurent.
2. Yves Desjardins, Histoire du Mile End, Québec: Les Ēditions du Septentrion, 2017, p. 22.
3. Island of Montreal property owners were required to pay dues to the Sulpicians every year until the seigneurial system was gradually abolished there, starting in 1840. The system was abolished in the rest of Quebec in a gradual process starting in 1854.
4. Louis Chaboillez, n.p. no 6090, 30 May 1804. A reference to the purchase also appears in J.A. Labadie, n.p. no 16733, 7 June 1875. This was the inventory of Stanley Clark Bagg’s Estate. It includes the name of the seller, the date of the sale and the notary who prepared the deed. This part of Mile End Farm is item #264.
5. Jonathan A. Gray, n.p. no 2874, 17 Oct. 1810.
6. Justin Bur, Yves Desjardins, Jean-Claude Robert, Bernard Vallée, Joshua Wolfe, Dictionnaire historique du Plateau Mont-Royal (Montreal, Éditions Écosociété, 2017), p 107.
7. Justin Bur, “À la recherche du cheval perdu de Stanley Bagg, et des origines du Mile End.” A la recherche du savoir: nouveaux échanges sur les collections du Musée McCord; Collecting Knowledge: New Dialogues on McCord Museum Collections. Joanne Burgess, Cynthia Cooper, Celine Widmer, Natasha Zwarich. Montreal: Éditions MultiMondes, 2015, p. 143.
8. Justin Bur, Yves Desjardins, Jean-Claude Robert, Bernard Vallée, Joshua Wolfe, Dictionnaire historique du Plateau Mont-Royal (Montreal, Éditions Écosociété, 2017), p 271.



