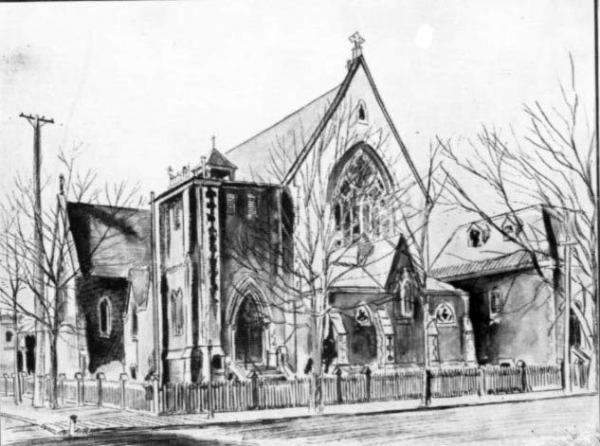Horses were a common part of daily life in turn-of-the-century Montreal. Tradesmen delivered milk and other items by horse and cart, fire engines were horse-drawn, and many people got around the city in horse-drawn carriages in summer and sleighs in winter. For those who could afford it, horseback riding, horse racing and horse shows were also popular.
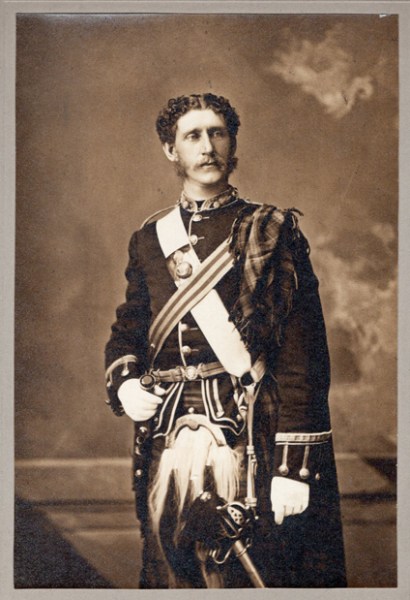
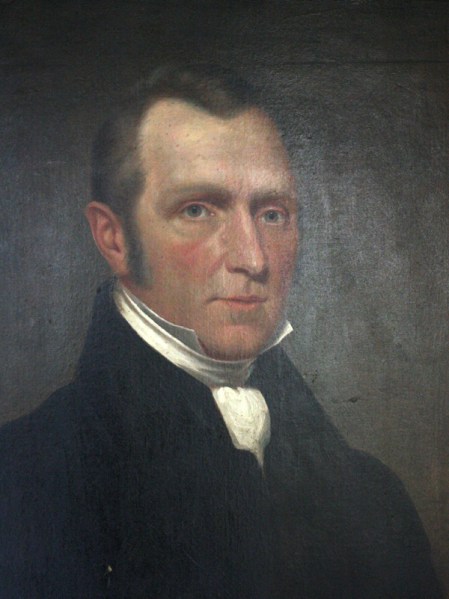
My great-grandfather Robert Stanley Bagg (1848-1912) was a skilled rider and every spring in the early 1900s, he and his wife, Clara, attended the Montreal horse show, held in suburban Westmount. Hunters, jumpers, harness horses and ponies competed for honours, but the show seems to have been more of a social activity than a sporting one, and proceeds from a tea served during the afternoon’s events were donated to the Society for Prevention of Cruelty to Animals.

The Montreal Star published columns of names of attendees, and in 1904, the paper noted that R. Stanley Bagg had a private viewing box. Perhaps, like other boxholders, he and Clara entertained guests at dinner prior to the evening events.
Two years later, the Star reported that Clara, dressed in green tweed with a black hat trimmed with white, attended the show with her sister-in-law Amelia Norton, in a purple dress and a white hat, and her daughter Evelyn, in a grey homespun dress and a pale blue hat, trimmed with white.1
Stanley was still riding at age 59 when was injured in an accident on Mount Royal, the mountain that rises behind the city center. The Star reported that he was riding on rough ground near the park ranger’s house when his horse stumbled on a rock, fell and rolled over on one side, pinning Mr. Bagg beneath him. Two men who happened to be nearby helped him get up and encouraged him to rest for a few minutes before riding home. Stanley had sprained his shoulder, hit his head and his face was badly scraped, however, he soon recovered.2
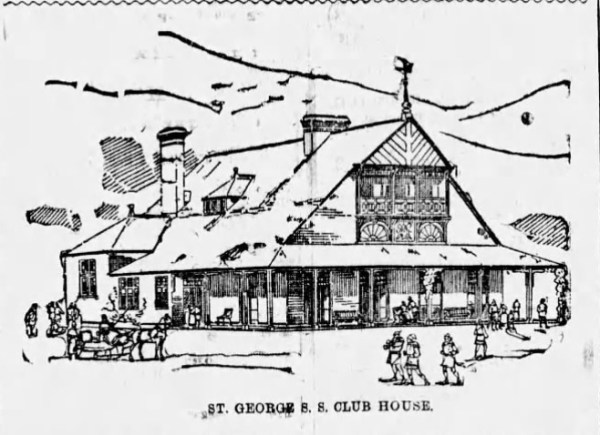
Snowshoeing was also a popular sport in Montreal, and one of Stanley’s favourite winter activities. Between the end of November and the beginning of March, the city’s rival snowshoeing clubs competed in races, held weekly “tramps” over the mountain and organized longer excursions to other locations on the Island of Montreal. Club social activities usually included an annual dinner, charity fundraisers and lots of singing. Stanley was a member of the St. George Snowshoe Club, and it had its own club song with a chorus that began, “Hurrah! Hurrah! It’s jolly on the snow. Hurrah! Hurrah! The stiffest storm may blow.…”3
Stanley was on his club’s building and furnishing committee, overseeing the construction of a new clubhouse at Côte St. Antoine. The building was constructed in the early English stye of architecture, with spacious verandas on all sides, a high-pitched roof with dormers and a square entrance hall that gave way to an assembly room with a huge fireplace and large windows overlooking the veranda. When the club house held its grand opening on the evening of December 21, 1887, Stanley was among those who led the way from the Windsor Hotel downtown to the new building.4

When he wasn’t enjoying sports, Stanley, a lawyer, worked in the Bagg family real estate business. Family life was also important, especially when they were travelling together or on summer holida
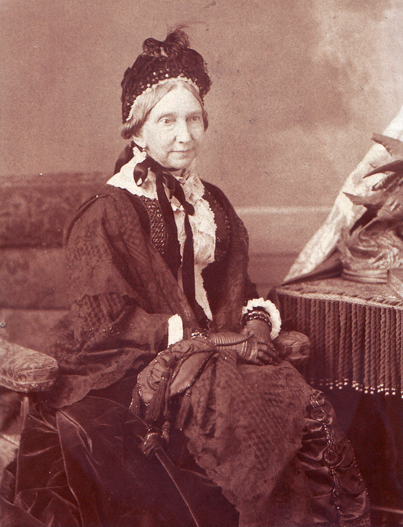
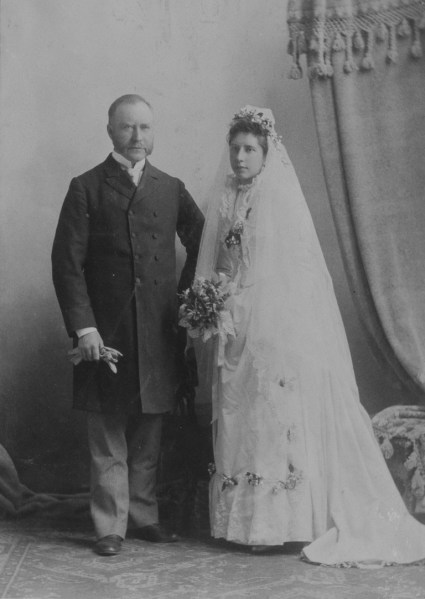
Stanley was married to Clara Smithers (1860-1946). One of eleven children, she was the daughter of Charles Francis Smithers, president of the Bank of Montreal, and his wife, Irish-born Martha Bagnall Shearman. When he started pursuing Clara in 1880, Stanley was age 32 and living at home at Fairmount Villa with his mother and sisters. (His father had died in 1873.) Stanley and Clara were married on June 8, 1882 at St. Martin’s Anglican Church in the presence of guests who included “the elite of our inner social circles.”5
The couple’s eldest child, Evelyn St. Clare Stanley Bagg, was born in 1883, and another daughter – my future grandmother – Gwendolyn Stanley Bagg was born in 1887. Their third child, Harold Fortesque Stanley Bagg, arrived in 1895.
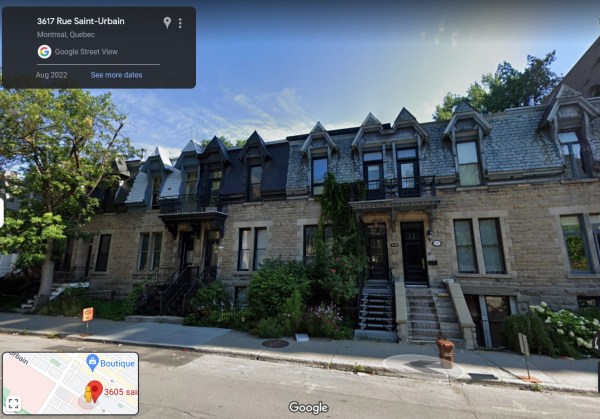
Having started a family, Stanley and Clara must have realized it was time to own a house of their own, so Stanley hired architect William McLea Walbank to build a house at 436 Saint-Urbain, near his mother’s home. It was completed in 1884.
According to a newspaper report, it was a handsome, well-finished brick villa of the Early English style of architecture, on Upper St. Urbain Street. The house contained all the modern conveniences of the time and was heated by Spence’s patent hot water furnace throughout. It claimed to be rat-proof. The bricks were all of Montreal manufacture and compared favorably with imported pressed bricks.
The family did not stay there long, however. In 1890, Lovell’s city directory listed Stanley as living in Georgeville, Quebec, while his sister Mary, the wife of stock broker Robert Lindsay, was living in the house on St. Urbain. Stanley had purchased a large house in Georgeville, on Lake Memphremagog, although it was probably a summer residence. Montreal was a very dirty and unhealthy city, especially in the heat, so many Montrealers left town during the summer months.
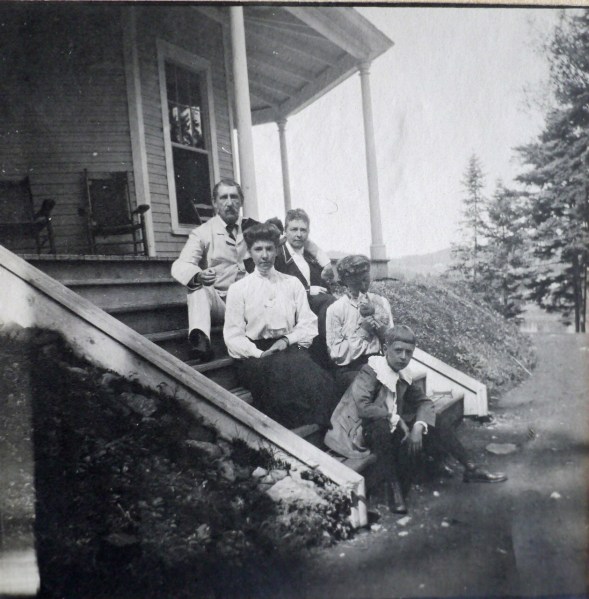

It does not appear that the Baggs owned the Georgeville house for many years. My grandmother acquired a camera around 1901 and her snapshots showed family summer vacations at Cacouna on the lower St. Lawrence River, at a rented a house on a lake near Ste. Agathe in the Laurentian Mountains, and at a summer hotel at Kennebunk Beach, Maine.
As for their city home, perhaps Stanley and Clara realized that their house on St. Urbain was not in the city’s most desirable neighbourhood. The place to live in Montreal was on the southwest slope of Mount Royal, an area known as the Golden Square Mile. Montreal was the financial and industrial capital of Canada, and businessmen were making fortunes and building mansions in that part of the city.
Stanley purchased a lot at the western edge of the Golden Square Mile, the corner of Sherbrooke Street and Côte des Neiges Road, and architect Walbank designed a new red sandstone house for him. Construction started in 1891, and the Baggs were living there by 1892. It was Stanley’s home until his death from cancer in 1912.6 Clara then divided the house into two apartments and remained there until she died in 1946.
Sources:
- “Horse Makes Farewell Bow Tonight,” The Montreal Star (Montreal, Quebec), May 12, 1906, p. 12, digital image, https://www.newspapers.com/image/738949773; accessed Aug. 4, 2024.
- “Mr. Stanley Bagg Injured in a Riding Accident,” The Montreal Star, (Montreal, Quebec), Nov. 25, 1907, digital image, https://www.newspapers.com/image/739434091; accessed Aug. 3, 2024.
- Hugh W. Becket, The Montreal Show Shoe Club, its history and record. With a synopsis of the racing events of other clubs throughout the Dominion from 1840 to the present time. Montreal, 1882, printed by Becket Bros. p. 459 https://ia800202.us.archive.org/8/items/cihm_03537/cihm_03537.pdf
- “Snowshoeing; The Red Cross Knights; St. George’s Snowshoe Club Inaugurated Last Night,” The Gazette, (Montreal, Quebec), Dec. 21, 1887, p. 8, digital image, https://www.newspapers.com/image/419349867; accessed Aug. 3, 2024.
- “Marriage Chimes: Fashionable Wedding at St. Martin’s Church Yesterday,” The Gazette, (Montreal, Quebec), June 9, 1882, p. 3.
- “R. Stanley Bagg Died Yesterday,” The Gazette, (Montreal, Quebec), July 23, 1912, digital image, https://www.newspapers.com/image/419604976, accessed Aug. 4, 2024.