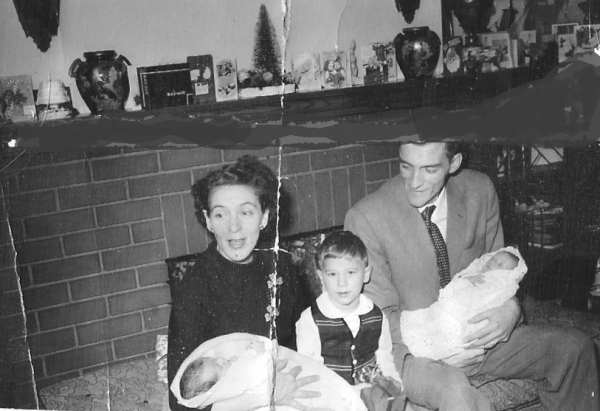
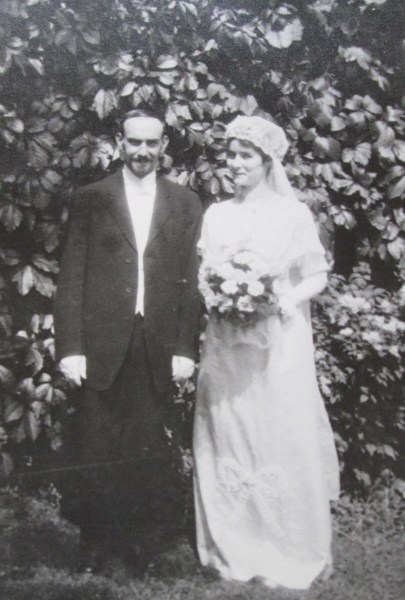
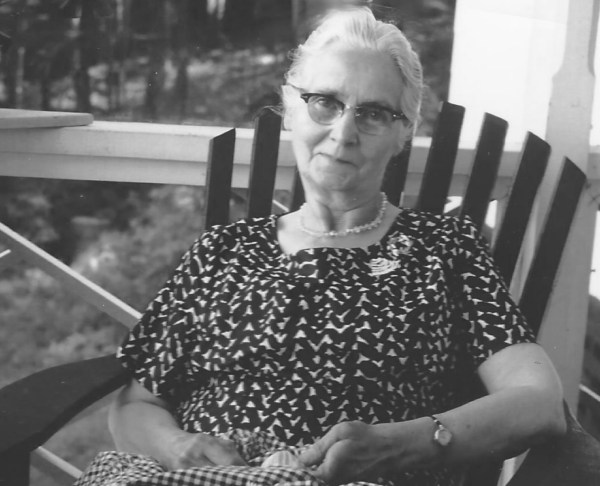
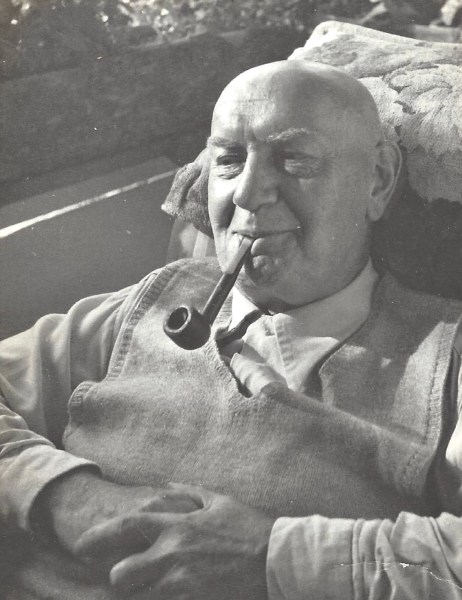
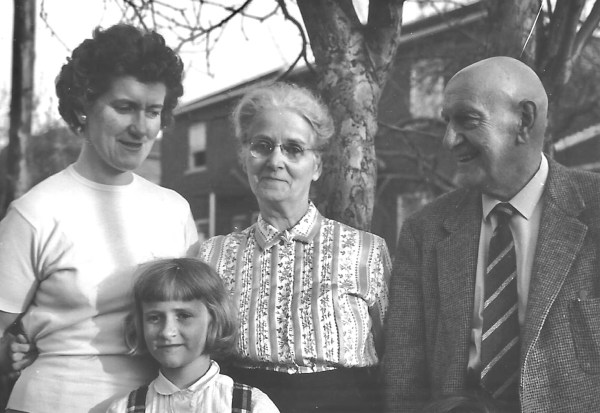
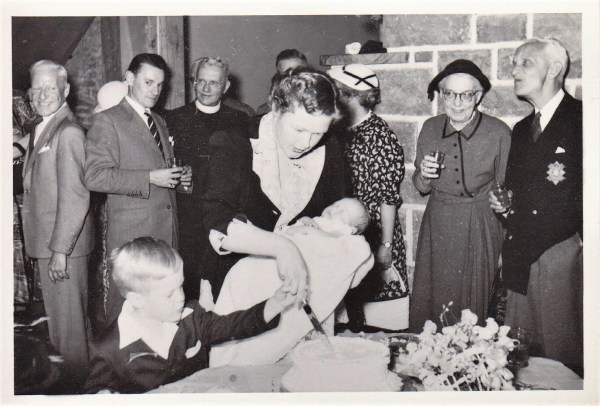
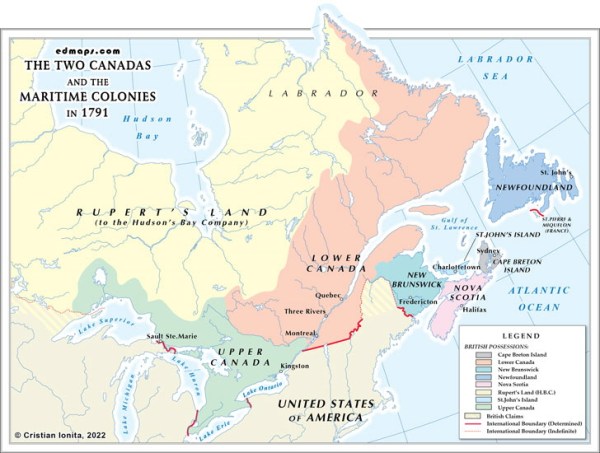
My father, Edward McHugh, didn’t really talk about his family’s trip of a lifetime. After all, Dad wasn’t even born yet. But it must have been discussed by everyone when he was a boy. In 1911, the first member of the family, Mary Ann McHugh, moved from Dundee, Scotland to Montreal.
At the time, booking agents in the United Kingdom advertised and recruited potential immigrants to Canada. There was an acute need of domestic help and agricultural workers. Between 1890 and 1920, Canada experienced its third wave of immigration and its peak was between 1911 and 1913, just before World War I.1 The following type of advertisement was common in the newspapers.2

Maybe one of these advertisements gave the McHugh family the idea to emigrate to Canada. Or maybe Mary was ready for an adventure. She was just 21 when she disembarked from the SS Grampian that had left Glasgow on June 24, 1911 and arrived in Quebec City on July 9, 1911. She would have had a medical exam when she arrived to ensure that she was in good health and did not have an infectious disease. Conditions for immigration to the colonies were well known in the United Kingdom. The February 11, 1911 edition of the Hamilton Observer, in its article, Canadian Notes, People Prohibited, details the reason some potential immigrants could expect to be refused by Canada. The article explains the booking agent’s liability for the immigrants that arrived in Canada for a period of three years following their arrival:
“The following classes of people are prohibited from landing … feeble minded, idiotic, insane, or who have been insane within five years, afflicted with any loathsome, contagious, or infectious disease; anyone who is a pauper, who is destitute, who is a professional beggar or vagrant.”3
All of the members of the McHugh family worked in the jute mills in Dundee. The 1911 census indicates Mary was a jute weaver, which probably meant that she operated a jute weaving machine.4 She lived with her mother, Sarah Jane McLaughlin, and her brothers, Edward and Francis. They lived at 1 Tait Lane, Dundee. Her other brother, Thomas, my grandfather, lived with his wife and seven children at 9 Tait Lane.
The picture below shows the jute weaving machine.5

Mary must have been satisfied with her new life in Montreal, Quebec. Within a year, her mother and her two brothers, along with my grandfather, had followed her to Canada. Six months later, my grandmother, Elsie Orrock, and her seven children joined her husband, Thomas, in Montreal.
The McHughs lived close together in Dundee and they also lived close together in Verdun, Quebec. While I will never know for sure why they decided to emigrate, I can guess that they wanted a life that was not as hard as the one working in the jute mills. There are a few clues that this was not a spur of a moment decision but a planned family decision.
Mary left first and, if it did not suit her to live in Canada, she would have been able to easily return to Dundee. Her mother and brothers were still there. By the time her mother emigrated, along with her three sons, they arrived with $150 CAD, about $4,750 in today’s dollars. Browsing through the passenger lists, I can see that they had a lot more money than many of their fellow passengers. 6 They were not a rich family, so this amount of money would have taken some time to save up.
Coincidentally my grandfather joined the Freemasons in 1910 and achieved a Master Mason diploma and a Mark Mason diploma.7 By that time, he already had six children. He worked long hours in the jute mill, including Saturdays. Why would he join the masons when he was already a very busy man providing for his family, plus taking care of his widowed mother, and his siblings who still lived at home? There is no evidence that he ever joined the masons when he arrived in Canada. I believe that it is possible that he joined the masons to in case he needed the contacts to find employment. As he quickly found work, his busy family life prevented him from pursuing his membership in the masons.
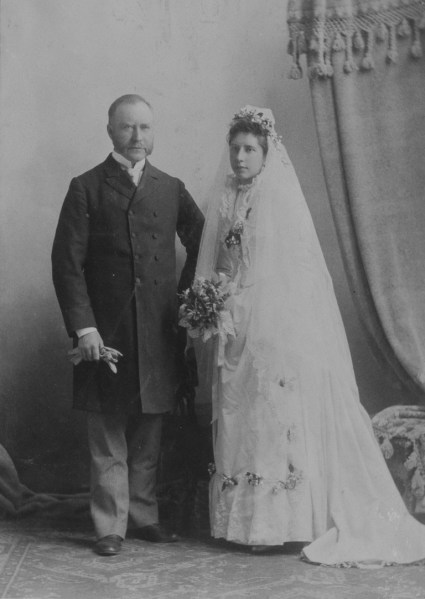
Only one of my grandfather’s siblings stayed in Scotland, Sarah Jane McHugh. She was not living with the other McHughs at the time of the 1911 census. But she remained close to the family. Surprisingly, she travelled to Montreal to be a witness at her brother’s wedding at the Notre Dame Basilica in Montreal on May 8, 1913.8 That would have been quite a trip for Sarah Jane to make.
- Wikipedia, Immigration to Canada, https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Immigration_to_Canada, accessed 27 September 2023.
- Irvine Herald and Ayrshire Advertiser (Irvine, Strathclyde, Scotland) · 13 Oct 1911, accessed Newspapers.com, downloaded 24 August 2023.
- The Hamilton Advertiser (Hamilton, Strathclyde, Scotland) · 11 Feb 1911, accessed Newspapers.com, downloaded 24 August 2023.
- Scotland’s People, National Records of Scotland, 1911 Census, Sarah Jane McHugh, downloaded 23 June 2019.
- V&A Dundee Design Museum, Women’s Day tweet, 6 March 2020.
- Passengers lists for S.S. Grampian arriving in Port of Quebec, May 21, 1912, Library and Archives Canada, https://www.bac-lac.gc.ca/eng/discover/immigration/immigration-records/passenger-lists/passenger-lists-1865-1922/Pages/image.aspx?Image=e003578022&URLjpg=http%3a%2f%2fcentral.bac-lac.gc.ca%2f.item%2f%3fid%3de003578022%26op%3dimg%26app%3dpassengerlist&Ecopy=e003578022, accessed February 3, 2022.
- Thomas McHugh, registration of the Grand Lodge of Scotland, dated 25 August 1910.
- Registration of marriage of Francis McHugh and Helen Smith, 8 May 1913, downloaded 6 January 2022.